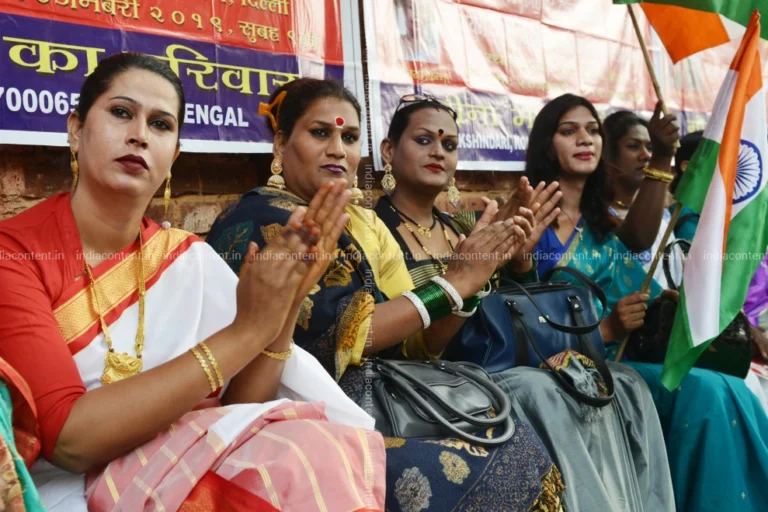
lifestyle of transgender individuals in India, like in other parts of the world, varies depending on factors such as location, socio-economic status, and individual circumstances. Life Style of Transgender People However, many transgender people face common challenges related to acceptance, discrimination, and access to basic rights and opportunities.
Life Style of Transgender People in India:
Life Style of Transgender People in India Transgender people in India are a part of the larger gender minority community. These individuals may not identify with the gender assigned to them at birth and often seek to express their gender in ways that feel true to themselves. In India, transgender people are sometimes referred to as “hijras,” a term that has a long history in South Asia, but the community includes many other identities beyond this term.
Know Life Style of Transgender People in India .Despite a rich cultural history where transgender people were once revered in certain aspects of Indian society (such as in some religious rituals and royal courts), the reality today is often different. Many transgender individuals experience significant social stigma, exclusion, and discrimination. They may be rejected by their families, face difficulty in finding employment, and are often denied access to education and healthcare. As a result, many transgender people are forced to live on the margins of society.

Challenges Faced by Transgender People:
- Discrimination and Stigma: Transgender individuals often face prejudice and discrimination in schools, workplaces, and even in their families. They may be bullied, harassed, or excluded because of their gender identity. This discrimination can lead to mental health challenges such as depression and anxiety.
- Lack of Employment: Due to societal stigma, many transgender people struggle to find regular employment. As a result, some are forced to engage in begging or sex work to survive. This lack of financial independence makes it harder for them to lead stable and dignified lives.
- Healthcare Access: Transgender people often face difficulties in accessing appropriate healthcare. Doctors and medical professionals may lack knowledge about transgender-specific health issues, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or gender-affirming surgeries. This lack of care can have serious consequences for their well-being.
- Legal Recognition: Though India has made strides in recognizing transgender rights, such as the landmark 2014 Supreme Court ruling that recognized transgender people as a “third gender,” challenges remain in ensuring full legal protection and equal rights. The process for legal gender change and accessing social services is still cumbersome for many.
- Education: Many transgender people face exclusion in educational institutions, either through bullying or institutionalized discrimination. This leads to lower educational attainment, which limits their career opportunities.

Government’s Responsibility:
The government of India plays a crucial role in improving the lives of transgender individuals by ensuring their rights are protected and by providing access to opportunities that allow them to live with dignity. Some of the key responsibilities of the government in supporting transgender people are:
- Legal Protection: The government must ensure that transgender people are legally recognized and protected from discrimination. The 2014 Supreme Court ruling was a positive step, but more needs to be done to implement laws that guarantee equal rights in employment, education, healthcare, and other areas of life. The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, passed in 2019, aims to provide some legal safeguards, but implementation remains a challenge.
- Healthcare Access: The government must make healthcare services more inclusive by training medical professionals about transgender-specific needs. Hospitals and clinics should offer gender-affirming care, including hormone therapy and mental health support. Transgender people should also have access to affordable healthcare without facing discrimination.
- Education and Employment: The government should ensure that transgender people have equal access to education and employment opportunities. This includes creating safe educational environments where transgender students are not bullied or marginalized. Additionally, public and private sectors should be encouraged to hire transgender people, and programs should be implemented to help them gain the necessary skills for the workforce.

- Social Welfare Programs: The government can help improve the economic situation of transgender individuals by providing access to social welfare programs. This includes pensions, healthcare, and housing schemes. Special programs aimed at training transgender people in various skills and supporting small businesses could also help them become financially independent.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The government should promote public awareness and education to reduce stigma and increase acceptance of transgender people. Media campaigns, school programs, and community outreach can help shift public attitudes and make society more inclusive.

Transgender Awareness Campaigns in India
- Support for Families: Many transgender people are rejected by their families. The government should promote counseling and support services for families to help them understand and accept their transgender members, thus reducing familial exclusion.

Conclusion:
The lifestyle of transgender people in India is still marked by social exclusion, discrimination, and economic hardship. While the government has taken some steps to protect their rights, much more needs to be done. Ensuring legal protection, improving healthcare access, and promoting education and employment opportunities are crucial to improving the lives of transgender individuals in India. Through awareness and continued policy changes, India can work towards creating a society where transgender people can live freely, with dignity and equal opportunities.